Clipping Data
Clipping is a method of subsetting data. The clipping parameters can be specified as either a bounding box or another data layer.
- Clipping by Bounding Box
- Clipping Vector Data by Polygon
- Clipping Raster Data by Polygon
- Batch Processing
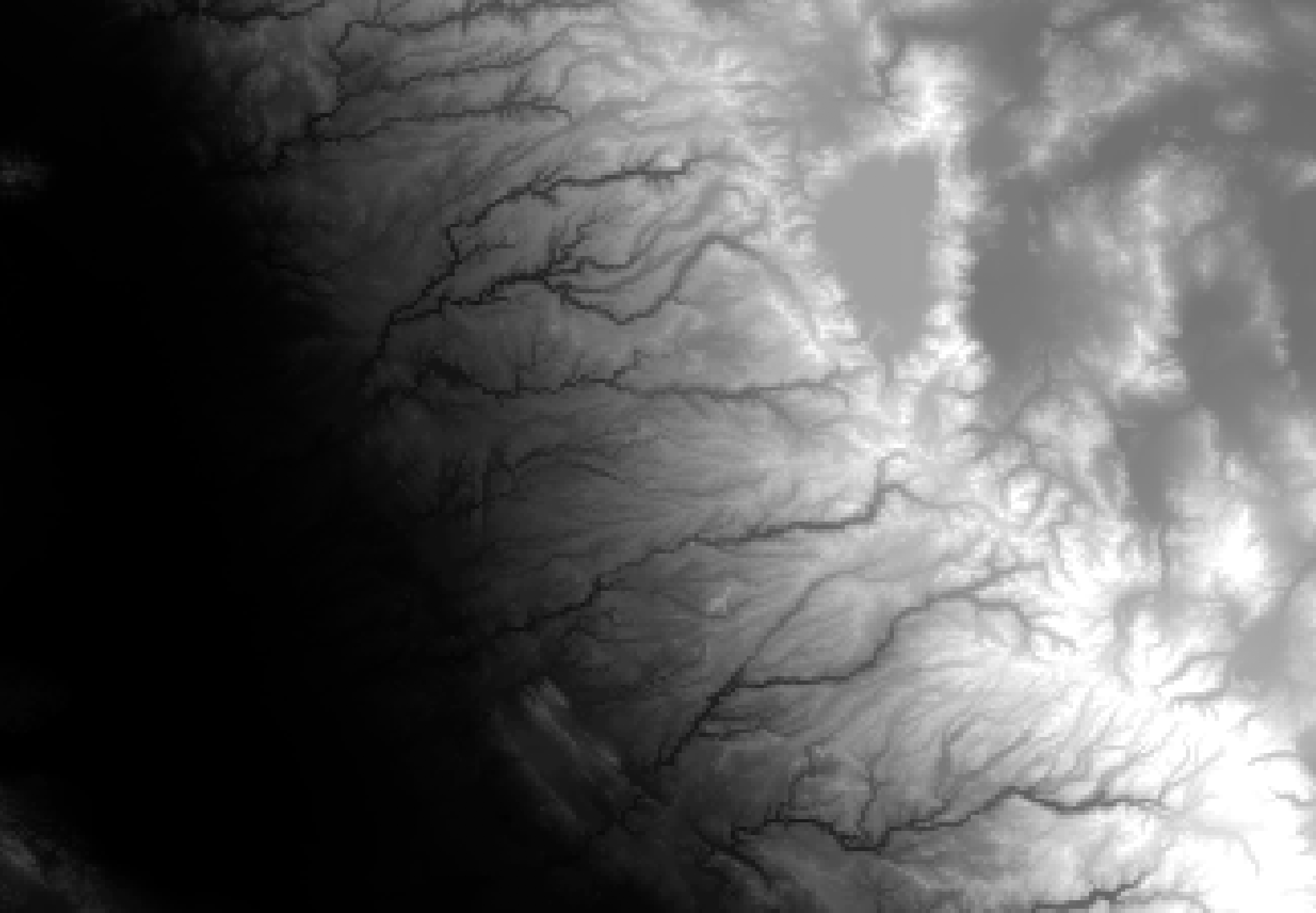
Clipping by Bounding Box
Use gdal_translate with the -projwin flag to specify the coordinates of a clipping extent (ulx uly lrx lry).
Let’s clip the DEM (gt30w140n40.dem) to a bounding box (-121.852 39.593 -119.119 37.675)
$ gdal_translate -projwin -121.852 39.593 -119.119 37.675 gt30w140n40_dem/gt30w140n40.dem gt30w140n40_clipped.dem
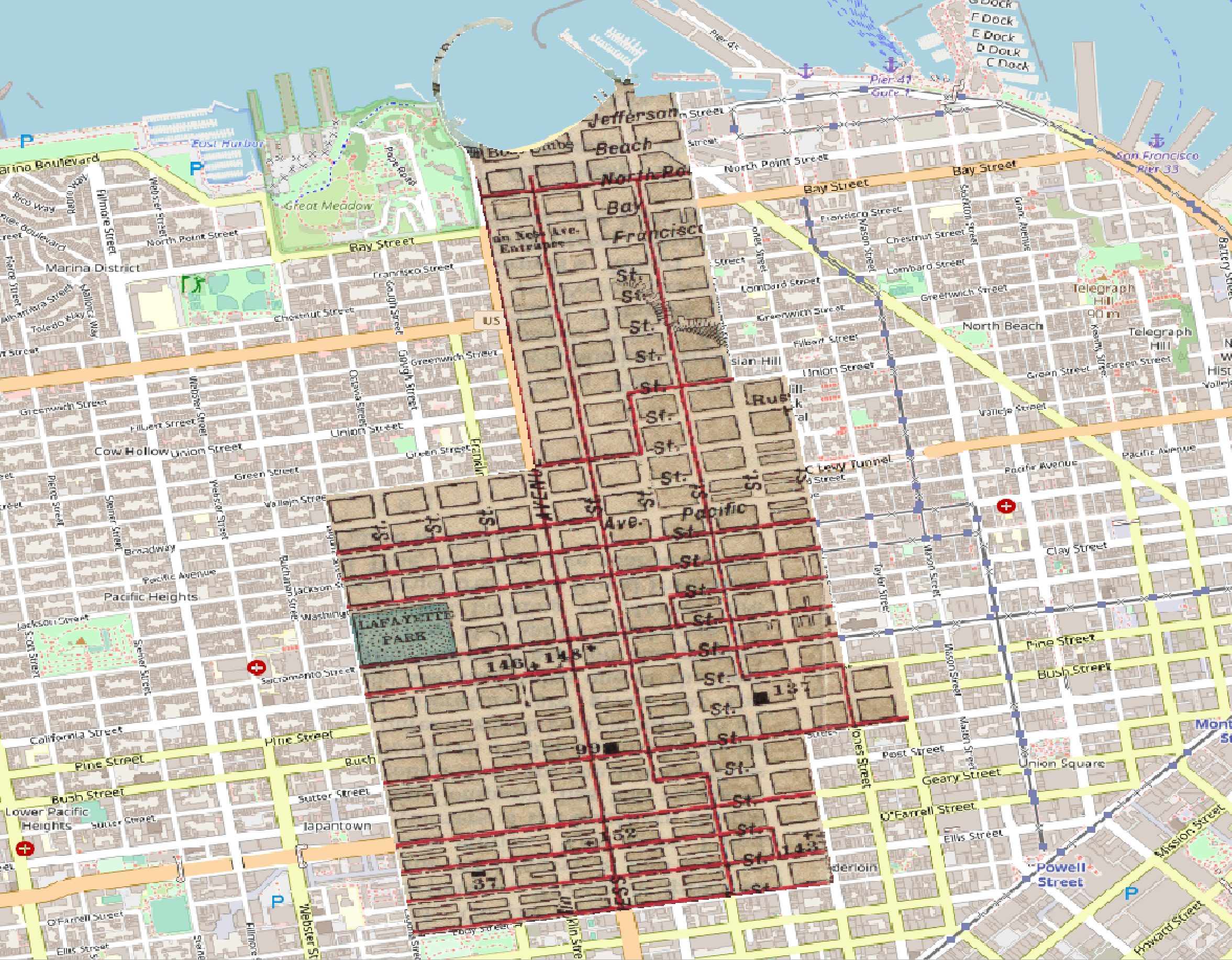
Clipping Vector Data by Polygon Boundary
Let’s clip the SF MUNI stops shapefile to contain only stops in the 94103 zip code. Use the -clipsrc flag to specify the clipping extent
$ ogr2ogr -clipsrc sf_94103.shp sf94103_muni_stops.shp sf_muni_stops.shp
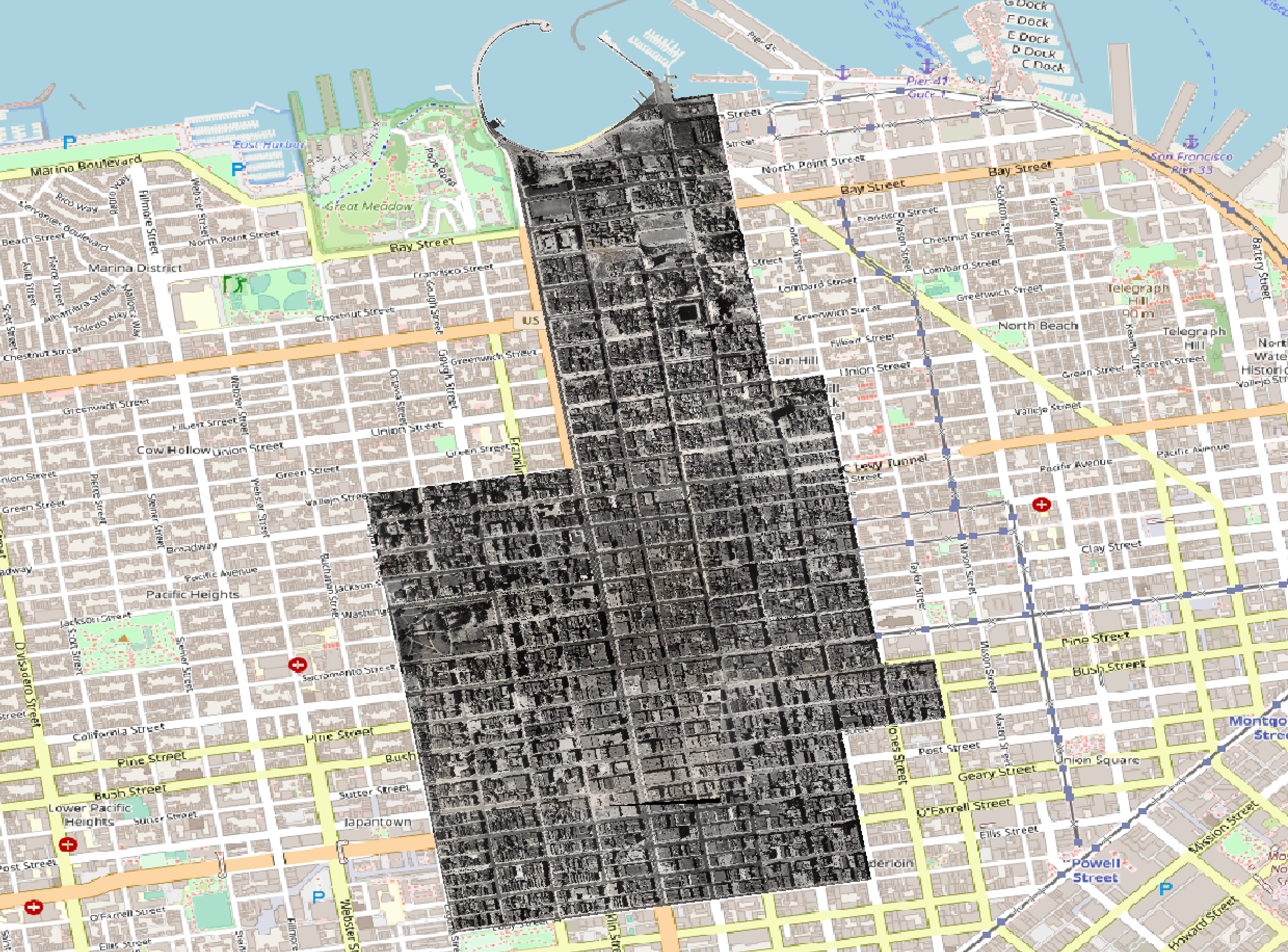
Clipping Raster Data by Polygon Boundary
Use gdalwarp with the -cutline flag to specify the clipping extent
Clip the 1987 San Francisco photo to the boundary of zip code 94109. Use the -crop_to_cutline flag to crop the extent of the new data to the cutline extent
$ gdalwarp -cutline sf_94109.geojson -crop_to_cutline SF1987_wgs84.tif SF1987_wgs84_clipped.tif
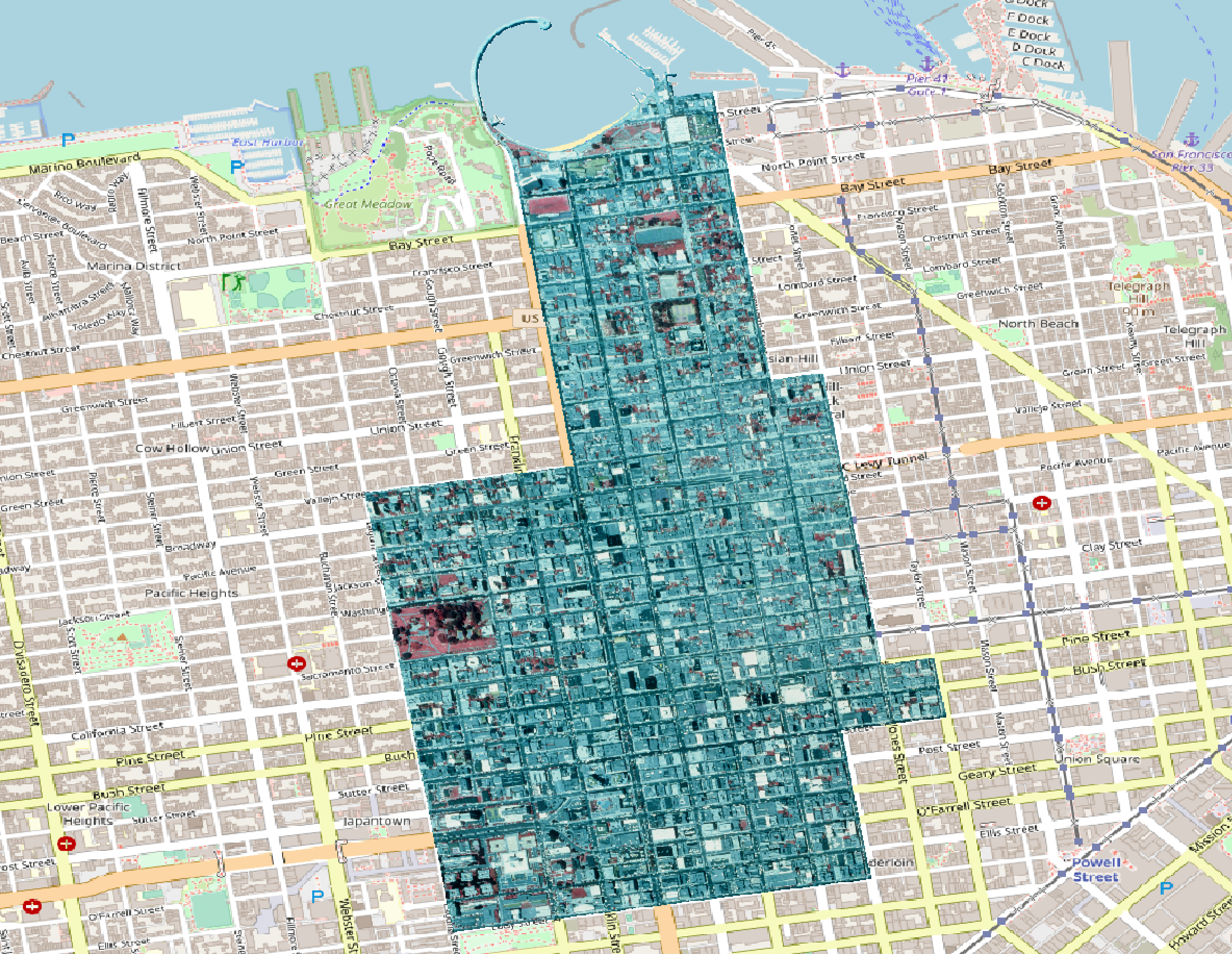
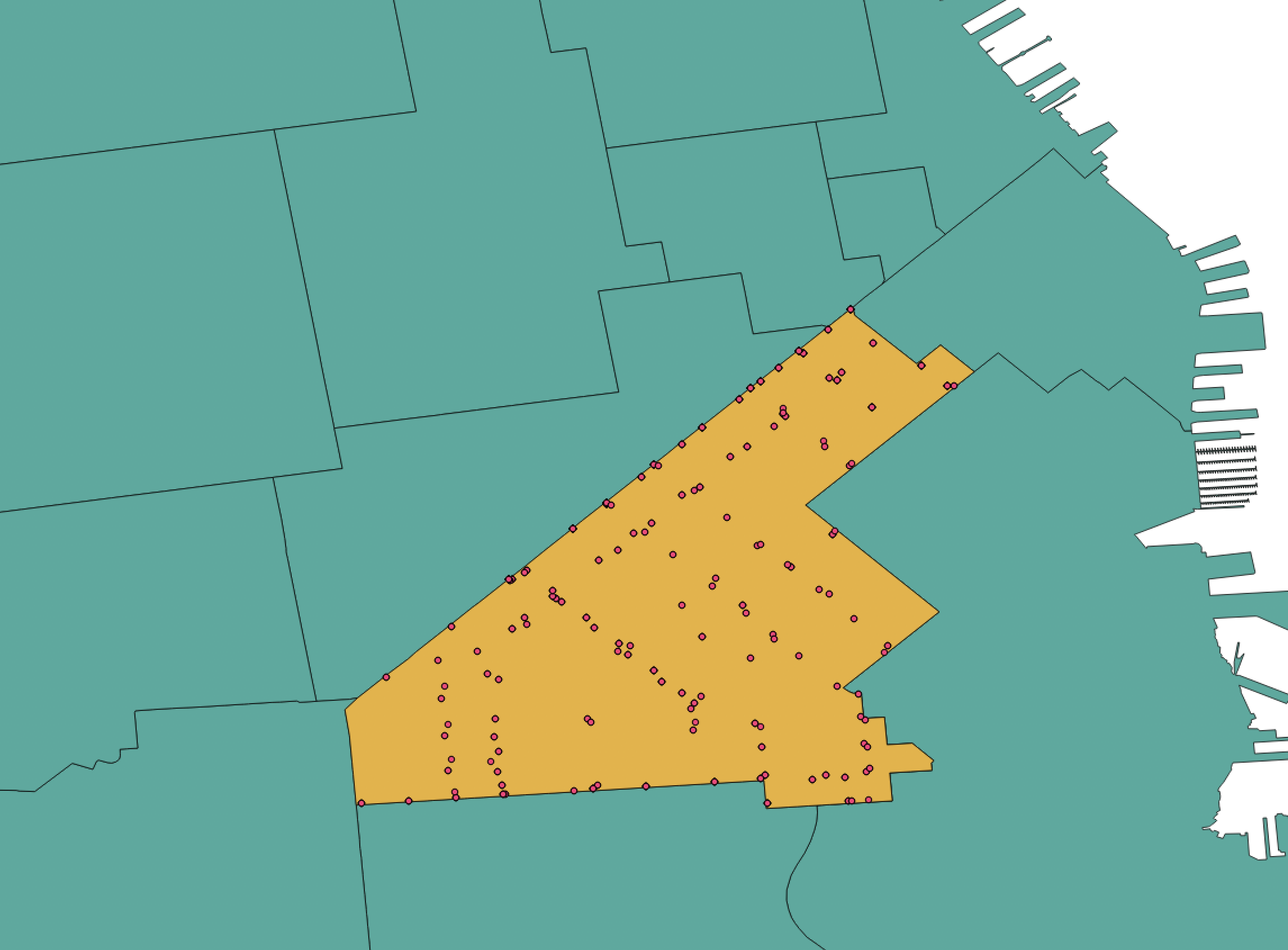
Batch Processing
Clipping multiple GeoTIFFs to a polygon boundary
$ python clipTiffs.py
import os
import fnmatch
CLIP= "sf_94109.geojson"
INPUT_FOLDER="."
OUTPUT_FOLDER= "clipped"
if not os.path.exists('clipped'):
os.makedirs('clipped')
def findRasters (path, filter):
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
for file in fnmatch.filter(files, filter):
yield file
break
for raster in findRasters(INPUT_FOLDER, '*.tif'):
newFile = raster[:-4]
inRaster = INPUT_FOLDER + '/' + raster
outRaster = OUTPUT_FOLDER +'/' + newFile + '_clipped.tif'
cmd = 'gdalwarp -q -cutline %s -crop_to_cutline -dstalpha -overwrite %s %s' % (CLIP, inRaster, outRaster)
os.system(cmd)